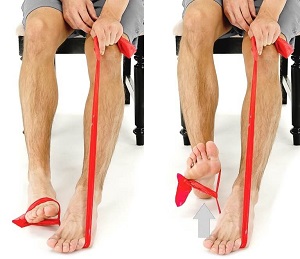
The influence of knee position on ankle dorsiflexion - a biometric study, BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders
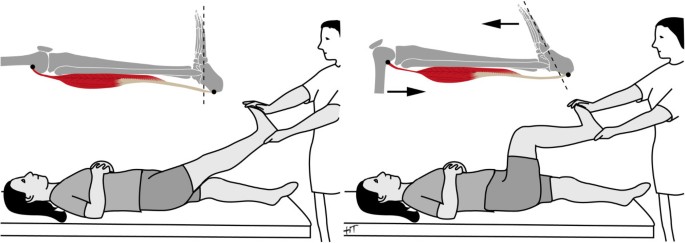
Background Musculus gastrocnemius tightness (MGT) can be diagnosed by comparing ankle dorsiflexion (ADF) with the knee extended and flexed. Although various measurement techniques exist, the degree of knee flexion needed to eliminate the effect of the gastrocnemius on ADF is still unknown. The aim of this study was to identify the minimal degree of knee flexion required to eliminate the restricting effect of the musculus gastrocnemius on ADF. Methods Bilateral ADF of 20 asymptomatic volunteers aged 18-40 years (50% female) was assessed prospectively at six different degrees of knee flexion (0°, 20°, 30°, 45°, 60°, 75°, Lunge). Tests were performed following a standardized protocol, non weightbearing and weightbearing, by two observers. Statistics comprised of descriptive statistics, t-tests, repeated measurement ANOVA and ICC. Results 20 individuals with a mean age of 27 ± 4 years were tested. No significant side to side differences were observed. The average ADF [95% confidence interval] for non weightbearing was 4° [1°-8°] with the knee extended and 20° [16°-24°] for the knee 75° flexed. Mean weightbearing ADF was 25° [22°-28°] for the knee extended and 39° [36°-42°] for the knee 75° flexed. The mean differences between 20° knee flexion and full extension were 15° [12°-18°] non weightbearing and 13° [11°-16°] weightbearing. Significant differences of ADF were only found between full extension and 20° of knee flexion. Further knee flexion did not increase ADF. Conclusion Knee flexion of 20° fully eliminates the ADF restraining effect of the gastrocnemius. This knowledge is essential to design a standardized clinical examination assessing MGT.

PDF) Validity and Reliability of the Achillometer®: An Ankle Dorsiflexion Measurement Device

IJERPH, Free Full-Text

Gastrocnemius tightness: A population based observational study - ScienceDirect

Reliability of Ankle Goniometric Measurements in: Journal of the

Kinematic analysis of gait in an underwater treadmill using land-based Vicon T 40s motion capture cameras arranged externally - ScienceDirect
Reliability of ultrasonographic measurement of muscle architecture

PDF) Influence of ankle joint position on angles and distances of the ankle mortise using intraoperative cone beam CT: A cadaveric study

Back foot influence on dorsiflexion using three different

Outcome measures of ankle dorsiflexion. a Position of the weightbearing

PDF] Measurement of ankle dorsiflexion: a comparison of active and passive techniques in multiple positions.
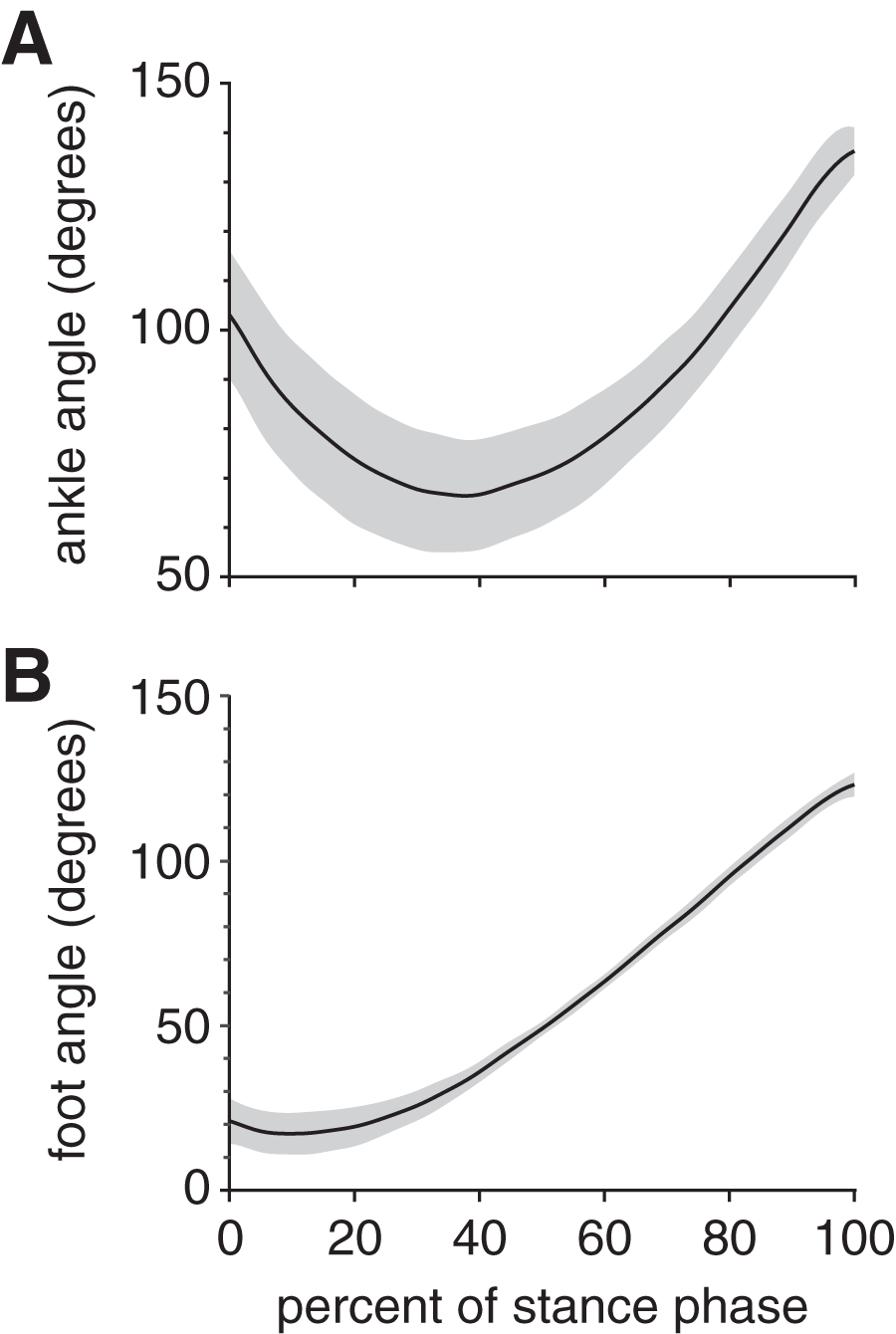
Rabbit hindlimb kinematics and ground contact kinetics during the stance phase of gait [PeerJ]

Longitudinal Evaluation of Hemiplegic Ankle Rehabilitation Efficacy by Wearable Inertial Sensor Systems with an Assortment of Machine Learning Algorithms

Back foot influence on dorsiflexion using three different