Breast Reconstruction Jeffrey R. Scott, Ph.D.. Definition Breast

Breast – Primary Function Breast Feeding a Newborn
Breast Reconstruction Jeffrey R. Scott, Ph.D.. Definition Breast Two milk-secreting, glandular organs on the chest of a woman; the human mammary gland.
Lobes, lobules, and bulbs are linked by thin tubes (ducts) Ducts lead to the centralized nipple (in center of the areola) Adipose tissue fills the space between lobules and ducts.
Anatomy – Breast (front view)
Anatomy – Breast (side view)
Often this includes the reformation of a natural-looking areola and nipple. The overall procedure involves the use of implants and/or relocated flaps of the patient s own tissue..
Definition Breast Augmentation Breast implant and/or fat-grafting mammoplasty procedures for correcting defects and/or enhancing the size, form, and feel of a woman’s breasts.
Definition Breast Cancer Cancer that forms in tissues of the breast, usually the ducts (tubes that carry milk to the nipple) and lobules (glands that make milk).
Scope Breast Cancer is the second leading cause of women, exceeded only by Lung Cancer. 1 in 8 women will be afflicted within their lifetime (12.5%). 1.3 Million New Cases are Diagnosed Annually Worldwide. Greater than 200,000 New Cases Diagnosed Annually in US. Responsible for 40,000 Deaths Annually in US Alone..
Non-invasive (in situ) - in which abnormal cancer cells remain within their place of origin, and have not spread to breast tissue around the duct or lobule. (i.e. DCIS – Ductal Carcinoma in situ (precancerous lesion), LCIS – lobular carcinoma in situ..
Invasive (metastatic) - in which abnormal cancer cells spread outside the membrane that lines a duct or lobule, invading the surrounding tissues. - cancer cells can then travel to other parts of the body, such as lymph nodes. - Typically graded as stage I, II, III or IV based on severity of invasive spread form origin..
Ductal Carcinoma (most common) - in which abnormal cancer cells originate in the lining of the milk ducts. 2. Lobular Carcinoma - in which abnormal cancer cells originate in the lobules connected to the milk ducts. 3. Sarcoma (rare) (i.e. angiosarcoma) - in which abnormal cancer cells originate within the connective tissue (blood vessels, muscle, adipose).
Breast Cancer Staging: Size, Location, Spread Tumor Size
- The cancer has not spread to the lymph nodes. - The cancer has not spread outside the breast..
- The tumor is 5 cm in diameter, but the cancer has not spread to the axillary lymph nodes. (A) - The tumor is <2 cm in diameter, but the cancer has spread to no more than 3 axillary lymph nodes. (B) - No tumor is found in breast, but cancer cells are detected in no more than 3 axillary lymph nodes..
(A) - The tumor is <5 cm in diameter, but the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes, which are growing into each other or the surrounding tissues. (stroma) - The tumor is <5 cm in diameter, but the cancer has spread to lymph nodes above the collarbone. (B).
- cancer cells have spread to other areas of the body, i.e. bones, brain, liver and/or lungs. - called Metastasis.
Symptoms A breast lump or thickening that feels different than surrounding tissue. Bloody discharge from the nipple. Changes to the breast surface (i.e. dimpling, pitting) Inversion of the nipple. Peeling, Scaling, Flaking of the nipple of breast skin..
Over time, the cells can develop abnormalities (atypical hyperplasia) that make them different from normal cells, but not yet cancerous. The abnormal cells may continue to change in appearance and multiply, evolving into noninvasive (in situ) cancer or, eventually, invasive cancer. Invasive cancer can spread to other areas of the body through the bloodstream or the lymphatic system..
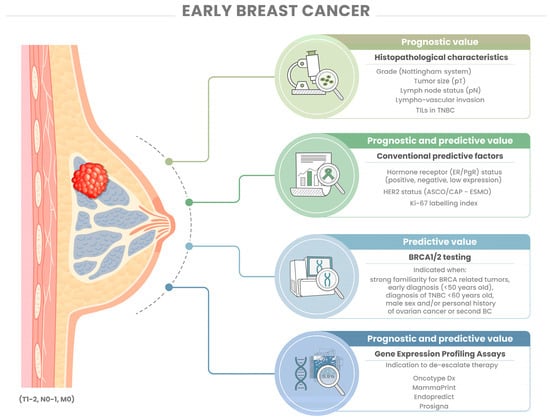
Diagnostic Tests for an Atypical Hyperplasia Physical Examination (Breast Exam) Blood Tests (to identify risk factor genes, i.e. BRCA 1/2) Mammogram Biopsy (pathological assessment) – in situ vs. invasive Lumpectomy (pathological assessment).
How is Breast Cancer diagnosed
How is Breast Cancer diagnosed Needle Biopsy Lumpectomy
Treatment Options Radiation Therapy Chemotherapy
Federal Breast Reconstruction Law Mandates that a health insurer which provides medical and surgical benefits with respect to a full or partial mastectomy, shall also be required to provide coverage for reconstructive and associated restorative procedures..
Overview of Breast Reconstructive Procedures - Video
Latissimus Dorsi Flap Breast Reconstruction
TRAM / DIEP – Fixed or Free Flap Breast Reconstruction
TRAM – Free Flap Breast Reconstruction
TRAM – Fixed Flap Breast Reconstruction
Breast Reconstruction – with Acellular Dermal Matrix / Silicone Expander
Permanent Implants: High-Molecular Weight Silicone Elastomer Shell (filled with Saline or Silicone).
1st generation implants-Thick, smooth-surfaced shells 2nd generation implants- Thinner shells, for a more natural feel Higher rupture rates Other innovations- Textured surface to prevent excessive fibrous tissue growth and to help fixation of implant within the breast Breast Implant - Biomaterials
Breast Implant – Biomaterials (fillers) Silicone Gel FilledSaline Filled
Breast Reconstruction – with Acellular Dermal Matrix / Silicone Expander Expander Pectoralis ADM Pectoralis Expander
Breast Reconstruction – with Acellular Dermal Matrix / Silicone Expander Pectoralis Muscle Allograft
Breast Reconstruction – with Acellular Dermal Matrix / Silicone Expander - Video
Silicone Expander Filling - Video
Breast Reconstruction – Silicone Expander Removal / Final Silicone Implant Insertion - Video
Novel Animal Models of Breast Reconstruction – Rat Model 12345
Novel Animal Models of Breast Reconstruction – Pig Model
Breast Reconstruction – Fat Grafting - Video
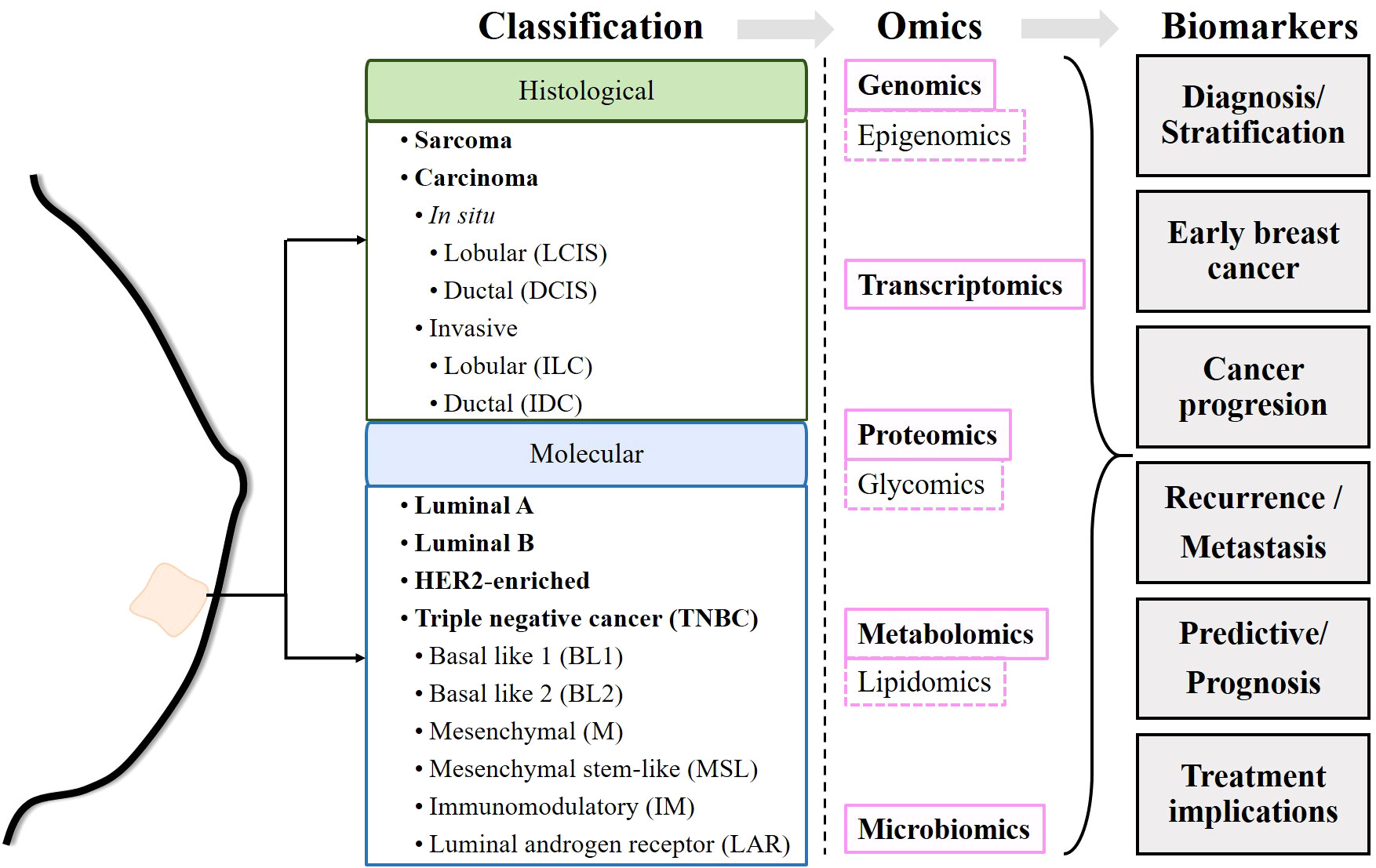
Frontiers Multiomics insights on the onset, progression, and metastatic evolution of breast cancer

Charles Scott Hultman, MD, MBA, FACS - Find A Doctor - UNC

Transcriptional regulation of normal human mammary cell heterogeneity and its perturbation in breast cancer

Reoperative Aesthetic and Reconstructive Plastic Surgery [2 ed.] 1576261808, 9781626239906, 9781626236134, 9781576261804

Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery

Cleveland Magazine - August 2023 by greatlakespublishing - Issuu

Dr. Rodney J. Rohrich, MD, Dallas, TX, Plastic Surgeon

Consult provider, don't panic about lump in breast - University of Mississippi Medical Center

Computational mechanobiology model evaluating healing of postoperative cavities following breast-conserving surgery - ScienceDirect

Figure 1. Anatomy of silicone implant rupture - ppt download

Breast Reconstruction Jeffrey R. Scott, Ph.D.. Definition Breast

Pioneering' breast cancer research yields more dollars in race for treatment, solutions - University of Mississippi Medical Center

Publications P4HB Biopolymer and Monfilament Surgical Scaffold

Frontiers Multiomics insights on the onset, progression, and metastatic evolution of breast cancer








:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Health-GettyImages-1342077649-8f68b0ae566d4429be7cdc4db0181ba7.jpg)