PDF] Compressive Ulnar Neuropathies at the Elbow: I. Etiology and
![PDF] Compressive Ulnar Neuropathies at the Elbow: I. Etiology and](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/cafadffa7184dea7f09a422611ec0e065559e273/2-Figure1-1.png)
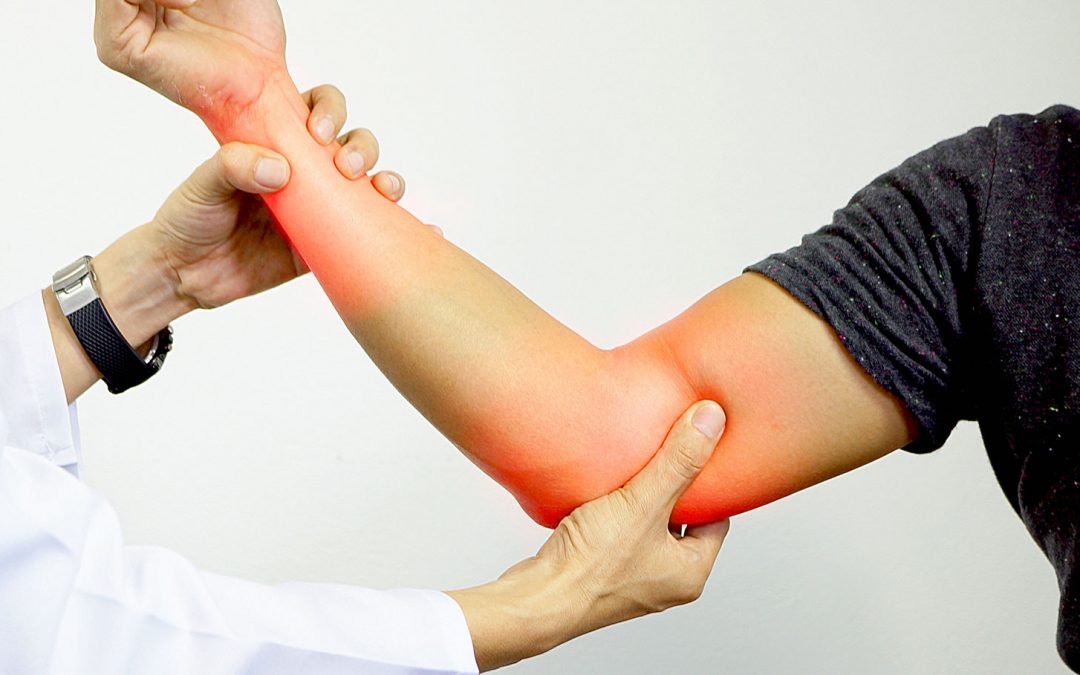
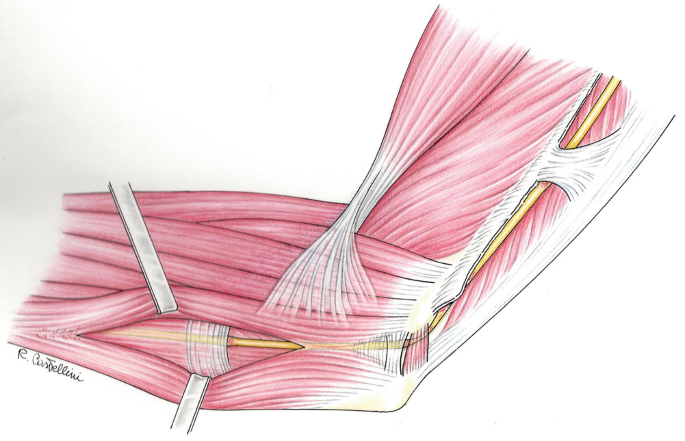
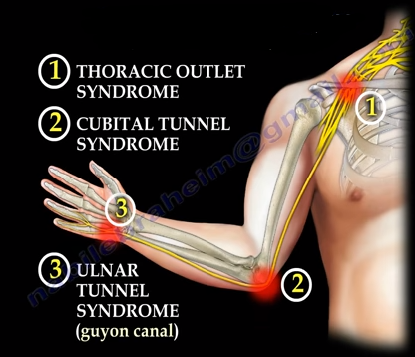
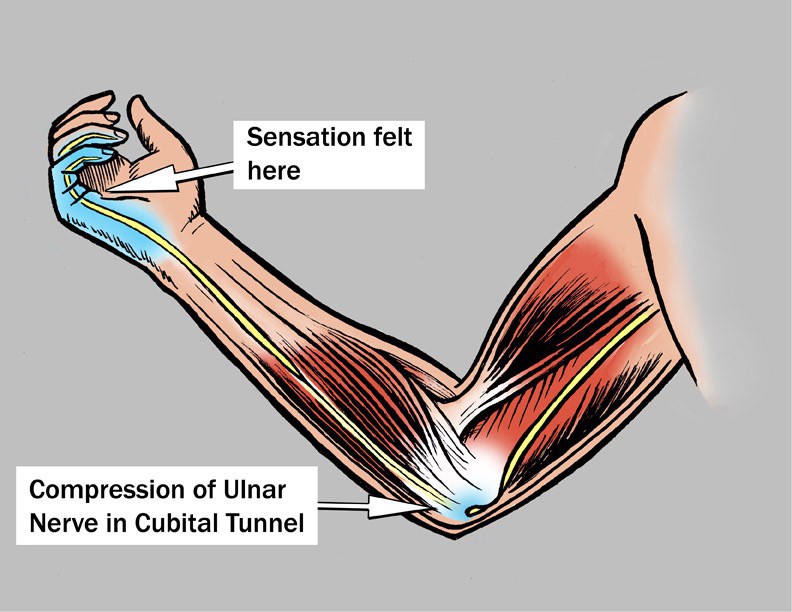
The differential diagnosis of ulnar neuropathies at the elbow includes lesions that cause additional proximal or distal nerve compression and systemic metabolic disorders. &NA; Ulnar nerve compression at the elbow can occur at any of five sites that begin proximally at the arcade of Struthers and end distally where the nerve exits the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle in the forearm. Compression occurs most commonly at two sites—the epicondylar groove and the point where the nerve passes between the two heads of the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle (i.e., the true cubital tunnel). The differential diagnosis of ulnar neuropathies at the elbow includes lesions that cause additional proximal or distal nerve compression and systemic metabolic disorders. A complete history and a thorough physical examination are essential first steps in establishing a correct diagnosis. Electrodiagnostic studies may be useful, especially when the site of compression cannot be determined by physical examination, when compression may be at multiple levels, and when there are systemic and metabolic problems.

Recalcitrant cubital tunnel syndrome
Ulnar Nerve Entrapment at the Elbow - Dr. Groh

A Review of Compressive Ulnar Neuropathy at the Elbow - ScienceDirect
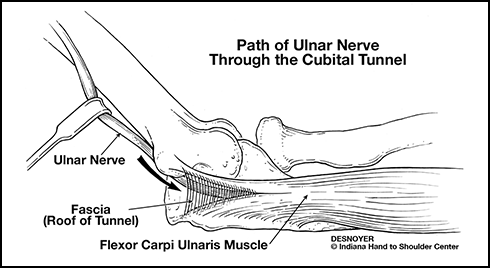
Ulnar Nerve Entrapment at the Elbow - Dr. Groh

Cubital tunnel syndrome, Radiology Case

PDF) Recalcitrant cubital tunnel syndrome Plastic and Aesthetic Research
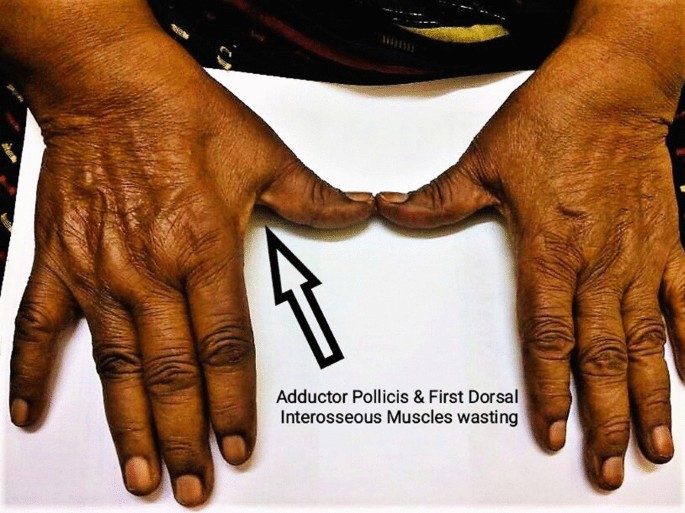
Cubital tunnel syndrome of the ulnar nerve caused by an epineural ganglion cyst: a case report and review of the literature, Journal of Medical Case Reports
Nerve Compression Syndromes of the Hand: Overview, Anatomy, Pathophysiology

Dynamic ulnar nerve compression at the elbow in a collegiate baseball player due to aberrant branch of the brachial artery - JSES Reviews, Reports & Techniques

Ulnar Neuropathy, PDF, Elbow

PDF] Entrapment Neuropathy of the Ulnar Nerve