Magnitude and determinants of knowledge towards pregnancy danger signs among pregnant women attending antenatal care at Chiro town health institutions, Ethiopia

The overall women’s knowledge of the danger signs of pregnancy was poor, and monthly income, distance to health facilities, and residence were determinant factors of mothers’ knowledge of pregnancy danger signs. Objectives: This study aimed to assess the magnitude and determinants of knowledge of pregnancy danger signs in Chiro town health institutions, Ethiopia. Methods: Institutional-based cross-sectional study was conducted among 395 systematically selected pregnant mothers. An interviewer-administered pretested questionnaire was used to collect data. The data were entered into EPI data version 3.1 and analyzed using SPSS version 22. Bi- and multivariate logistic regression analyses were used to identify determinant factors. Statistical significance was declared at p < 0.05. Results: Even though 58.0% of respondents recalled at least one danger sign of pregnancy, only 26.3% (95% confidence interval: 21.7–30.7) of the respondents had good knowledge of pregnancy danger signs. Residence (adjusted odds ratio = 2.43, 95% confidence interval: 1.50–4.00), distance to health facility (adjusted odds ratio = 2.11, 95% confidence interval: 1.28–3.47), and income (adjusted odds ratio = 1.99, 95% confidence interval: 1.22–3.33) were found to be significantly associated with mothers’ knowledge of pregnancy danger signs. Conclusion: The overall women’s knowledge of the danger signs of pregnancy was poor. Monthly income, distance to health facilities, and residence were determinant factors of mothers’ knowledge of pregnancy danger signs. Thus, the provision of information targeting pregnant women, their families, and the general community regarding danger signs of pregnancy is recommended to health care providers.

Spatial distribution and determinants of an optimal ANC visit among pregnant women in Ethiopia: further analysis of 2016 Ethiopia demographic health survey – Healthy Newborn Network

PDF) Knowledge About Danger Signs of Pregnancy and Associated Factors Among Pregnant Women in Debra Birhan Town, Central Ethiopia

Loop Tamirat Getachew

PDF) The Influence of Home Delivery on Maternal Mortality in Longido District in Tanzania: A Mixed Method Study
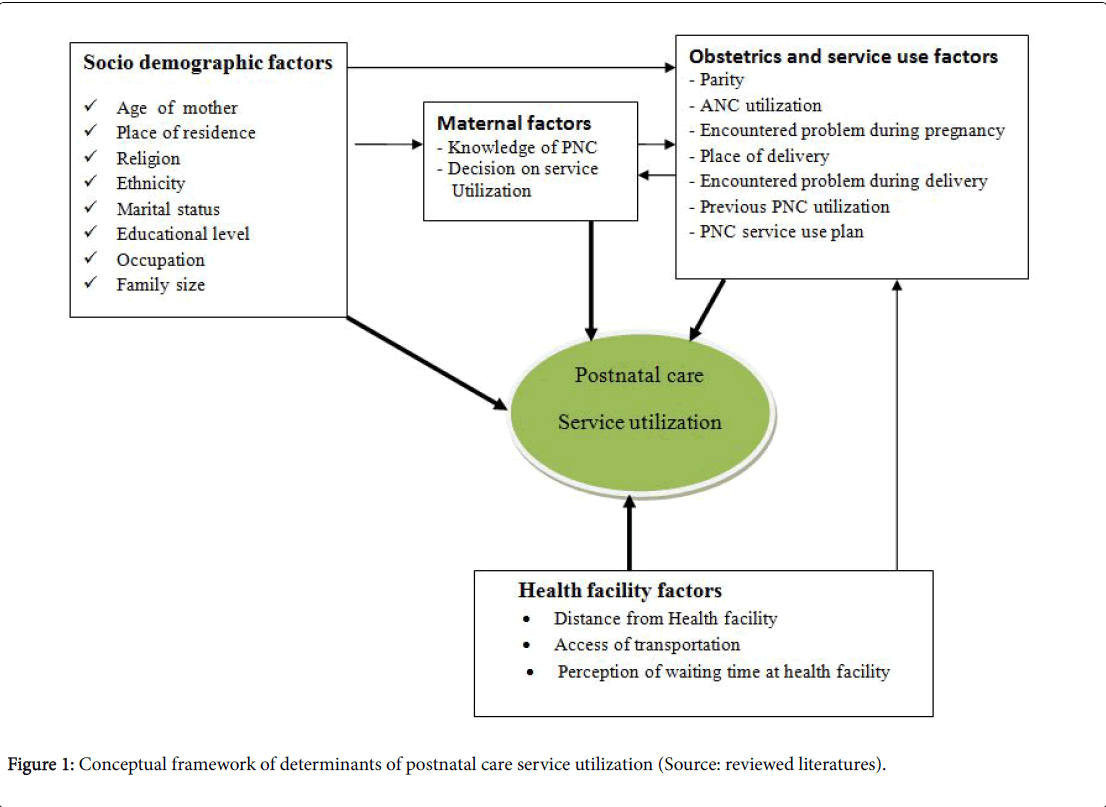
Determinants of Postnatal Care Service Utilization, Amigna Distri

Current Issue Volume 4, Issue 4, TEXILA INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PUBLIC HEALTH

Relation of education with level of awareness among women attending ANC

Knowledge of Danger Signs for Major Obstetric Complications Among Pregnant KwaZulu-Natal Women: Implications for Health Education - M. Hoque, M. E. Hoque, 2011

PDF) Magnitude and determinants of knowledge towards pregnancy danger signs among pregnant women attending antenatal care at Chiro town health institutions, Ethiopia

Perception of obstetric danger sign by marital status of women in

PDF) Magnitude and determinants of knowledge towards pregnancy danger signs among pregnant women attending antenatal care at Chiro town health institutions, Ethiopia

shows respondent Assessment on knowledge obstetric danger signs during

PDF) The Influence of Home Delivery on Maternal Mortality in Longido District in Tanzania: A Mixed Method Study
Adherence to iron and folate supplementation and associated factors among women attending antenatal care in public health facilities at Covid-19 pandemic in Ethiopia








